Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Lu, K.; Katsuyama, Jinya; Li, Y.
Nihon Kikai Gakkai M&M 2016 Zairyo Rikigaku Kanfarensu Koen Rombunshu (Internet), p.499 - 501, 2016/10
When conducting structural integrity assessments for reactor pressure vessels (RPVs) subjected to pressurized thermal shock (PTS) events, the stress intensity factor (SIF) is evaluated for a postulated surface crack in the inner surface of RPVs. It is known that the cladding made of a stainless steel is a ductile material which is overlay-welded on the inner surface, therefore, the plasticity of cladding should be considered in SIF calculations for a postulated underclad crack to ensure a conservation evaluation. Recently, the authors performed three-dimensional (3D) elastic and elastic-plastic FEAs for Japanese three-loop RPVs and proposed a rational evaluation method on SIFs of underclad cracks. In this paper, further studies were conducted to discuss the applicability of the proposed plasticity correction method. The effect of neutron irradiation was considered. In addition, different Japanese RPV geometries such as two-loop and four-loop RPVs were also investigated.
Nagai, Masaki*; Lu, K.; Kamaya, Masayuki*
Nihon Kikai Gakkai M&M 2016 Zairyo Rikigaku Kanfarensu Koen Rombunshu (Internet), p.481 - 483, 2016/10
In nuclear power plants, a number of cracks attributed to stress corrosion cracking (SCC) have been detected in welds made with nickel alloy weld metals. One of the characteristics of these cracks is that crack aspect ratio 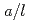 is greater than 0.5, where a is the crack depth and
is greater than 0.5, where a is the crack depth and  is the crack length. When a crack is detected in components of nuclear power plants during in-service inspection, flaw evaluation is conducted according to the requirement of codes such as JSME Rules on Fitness-for-Service for Nuclear Power Plants. Here, the stress intensity factor plays an important role for predicting crack growth behavior due to fatigue and/or SCC. Although several solutions of the stress intensity factor are already given in the JSME code, no solutions are available for the cracks with
is the crack length. When a crack is detected in components of nuclear power plants during in-service inspection, flaw evaluation is conducted according to the requirement of codes such as JSME Rules on Fitness-for-Service for Nuclear Power Plants. Here, the stress intensity factor plays an important role for predicting crack growth behavior due to fatigue and/or SCC. Although several solutions of the stress intensity factor are already given in the JSME code, no solutions are available for the cracks with 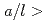 0.5. According to the current code, surface cracks with
0.5. According to the current code, surface cracks with 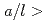 0.5 are characterized as semi-circular shape
0.5 are characterized as semi-circular shape 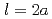 . To evaluate these cracks in a rational manner, several solutions have been proposed for cracks with
. To evaluate these cracks in a rational manner, several solutions have been proposed for cracks with 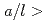 0.5. In this paper, comprehensive comparison was made between solutions for cracks
0.5. In this paper, comprehensive comparison was made between solutions for cracks 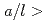 0.5, and benchmark analysis on SCC crack growth was performed.
0.5, and benchmark analysis on SCC crack growth was performed.
Kuroda, Masatoshi*; Kamaya, Masayuki*; Akita, Koichi; Yamada, Teruaki*; Shimasaki, Tomonori*; Tanigawa, Ryohei*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English